The current world is experiencing an enormous upsurge in technological developments. New innovations are being introduced on a day to day basis. The mother of these developments is usually the invention and innovation of classical programs that are totally advanced and manipulate the ongoing technological trends. The success of these programs is, however, the coding and algorithms used to develop such competitive programs. Therefore, for a successful and complete program, the exploitation of a proper and accurate algorithm is a must. Let’s discuss the top 10 algorithms or classes of the algorithms used widely in programming and development.
Contents
Top 10 algorithms used in programming
1. Hashing
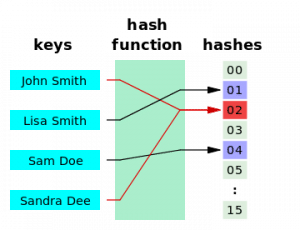
Currently involved in the detection and determination of an appropriate data by key and ID, a Hash lookup is a technique employed. With extended roles in the detection of errors, cache management, cryptography and effective lookup, the hash function maps the appropriate keys to values with precise efficiency. The function can also be used as a unique identifier for certain data sets and its math calculations can enable the creation of non-colliding data values. Normally it is applied in routers for IP address storage.
2. Search Algorithms
The search algorithms may either be applied to the linear data structures or graphical data structures. The linear search algorithms also are known as binary search are used to conduct efficient searches on sorted datasets with a time complexity function of O(log N). The Binary search divides the list into halves until it locates the required item and is normally used for git bisection debugging.
Also known as Depth/Breadth First Search, the algorithms for graphical data structures are a graph or tree enabled searching functions that locate required data sets in a traversing-tree model. The BFS is common in search engines, also used to build bots in artificial intelligence as well as locating the shortest paths between two cities.
3. Sort Algorithms
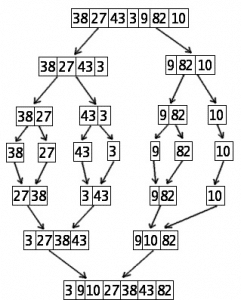
The sort algorithms are usually developed to place data in an organized manner. In QuickSort algorithm, the data components are compared against each other to determine their respective orders. It has the time complexity of O(nLogn) to perform enough comparisons. Radix Sort is, however, a faster technique than Quick Sort as it sorts the elements in a linear model with O(n) time complexity. The simplicity of the algorithm makes it much simpler and faster to carry out sorts. Other sorting algorithms include the merge sort, Bucket sort, and Counting sort.
4. Dynamic Programming Algorithms
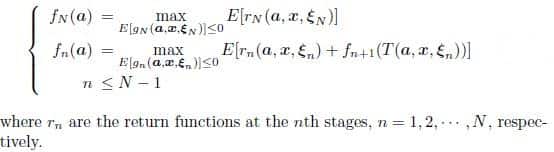
Dynamic programming is usually an intelligent problem-solving function that segregates complex
problems into smaller subproblems, solves them then build back into the complex problem with a memory of the smaller results to give the answer to the complex problem. Integrated to memorization that enables storage of memories of the previously solved problems, the subsequent time the same problem appears,
the problem is solved much faster.
5. Link Analysis
Commonly used in networking, link analysis offers the ability to correlate between different entities within a domain which is vital for the search engines. The algorithm uses a graphical representation and a complex matrix that links the similar bases within the domains present. Link analysis is common in the search engines like Google, as well as in the social media platforms such as Facebook, Twitter where extensive searches are carried out.
6. Modulo Arithmetic Algorithms
Many complex cryptographic algorithms are actually based on fairly simple modular arithmetic. In modular arithmetic, the numbers we are dealing with are just integers and the operations used are addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division. The only difference between modular arithmetic and the arithmetic you learned in your primary school is that in modular arithmetic all operations are performed regarding a positive integer, i.e. the modulus.
Examples:
- Basic and Extended Euclidean algorithms
- Euler’s Totient Function
- Modular Exponentiation
- Modular Multiplicative Inverse
- Chinese remainder theorem Introduction
- Chinese remainder theorem and Modulo Inverse Implementation
7. String Matching and Parsing Algorithms
The process of creating matching patterns is always vital in any networking domains and elements. The string matching algorithms are used in scenarios where patterns have to match in a long string or when a validation of a string by parsing over a predefined limitation is required. These matching and passing algorithms are commonly used in web development for URLs
8. Fourier Transform Algorithms
Fourier Transform and Fast Fourier Transform are simple yet very powerful algorithms. They are used for transforming signals from their time domain into their frequency domain and vice versa. The whole Digital networking including internet, WiFi, phone, computer, router, satellites, use these algorithms in one way or another to function. These are the must-know algorithms for electronics, computing or telecommunications degree program.
9. Disjoint Sets
Disjoint Sets are data structures that serve as helper structures within an algorithm to represent multiple sets within an individual array, with each item being a member of one of the many sets. Disjoint sets, therefore, represents connected components in graph algorithms as well as segmenting an image.
10. Integer Factorization
The integer factorization algorithm is a mathematical algorithm that provides a stepwise guideline on how to get the prime factors of a composite number. This algorithm solves the complex problems in cryptographic platforms that require factoring large composite integers.


