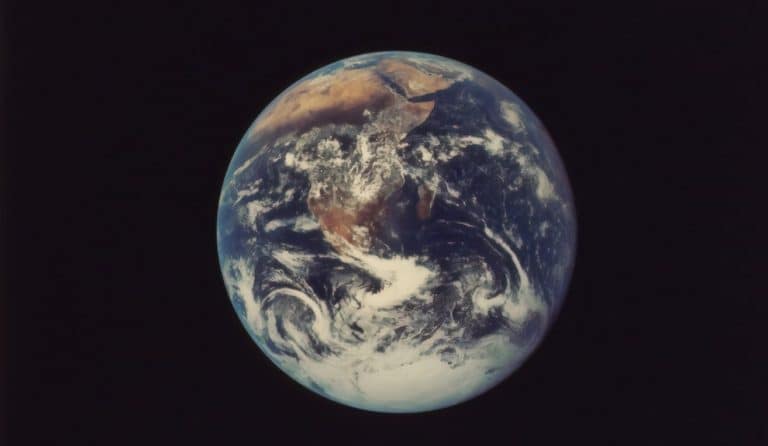
Earth observation projects allow scientists to gather important data about ecosystems and changes in weather patterns. Earth observation projects allow scientists to gather important data about ecosystems and changes in weather patterns. Sophisticated satellite cameras can also help find archaeological sites and help manage the effects of climate change.
In recent years, the satellite camera has become increasingly important as an important part of space technology. As satellite research has progressed collecting images of the Earth and measuring natural phenomena the technology itself has become easier and more sophisticated at the same time. Many space companies use satellite cameras for Earth observation projects, such as recording changes in weather patterns or analyzing natural ecosystems.
Contents
What is satellite camera technology?
Satellite cameras are remote sensing measuring devices that can be attached to satellites and sent into orbit. From orbits, these cameras are able to measure electromagnetic wavelengths and turn these into images or data that scientists can decipher. These types of cameras are also compatible with airplanes and drones. However, orbital satellites are the most effective way to perform global Earth observation.
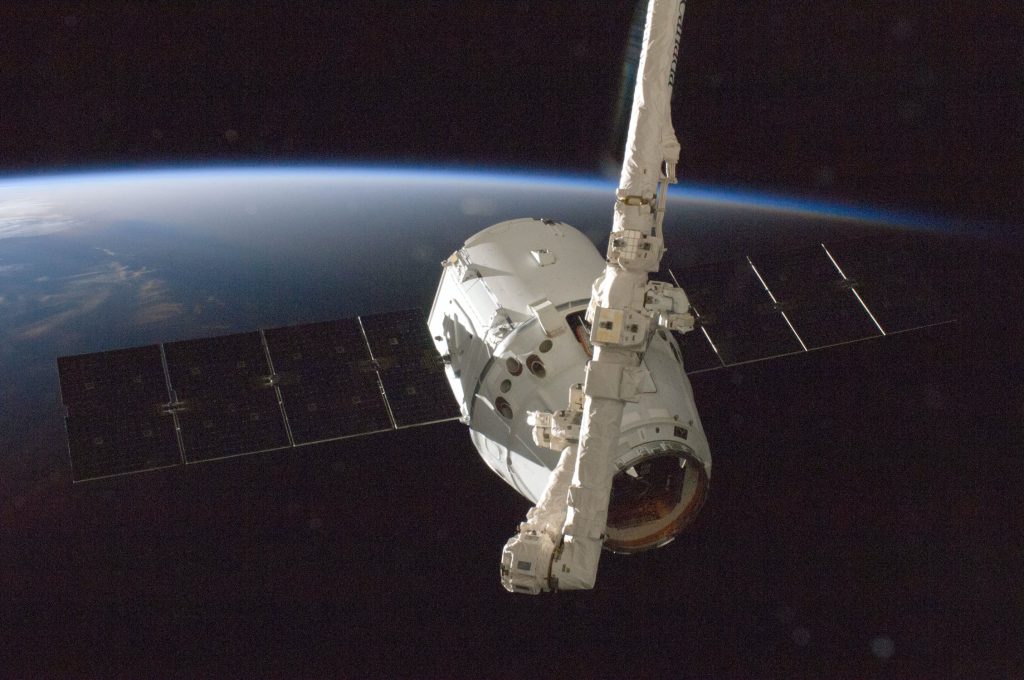
What does a satellite camera look like?
Satellite cameras can vary in terms of size, shape, and capacity of taking measurements. Often, satellite cameras look like regular space satellites with a large lens protruding from them. Others may have a disc-like shape.
Satellite cameras are usually grouped according to size. Large to medium cameras are between 500-1000kg. Meanwhile, mini-satellites weigh around 100-500kg. As satellite technology has progressed, nano or micro-satellite cameras have come on the market. These can weigh as little as 1kg.
Satellite cameras can be used to measure a variety of different phenomena for the purposes of Earth observation. Cameras that generate passive imagery do so by sensing emissions from the Earth’s surface, such as heat and light reflections from flora and fauna. The images produced by these cameras can be disrupted by cloud cover or by other emissions.
For higher resolution images, panchromatic and multi-spectral cameras are often used. Panchromatic cameras can produce grey, close-range images of Earth using infrared thermal sensors. Meanwhile, multi-spectral imaging refers to the process of generating photos using electromagnetic wavelengths, such as those from ultraviolet or infrared sources.
For those wondering how to use the satellite camera to generate data, many space companies use a mixture of different imaging types to create photos. For example, by blending panchromatic and multi-spectral images, scientists can create colored photos of Earth in high resolution. Another way that satellite cameras can capture images is by measuring water vapor and sensing water content in cloud formations. This type of satellite camera is known as a microwave radiometer or MRW.
What are earth observation cameras used for?
Earth observation and satellite imaging have a huge range of practical applications in a variety of fields. Uses also vary depending on satellite camera size and capacity. Some of the main uses for satellite cameras are conservation and ecological projects. Examples include:
Observing weather patterns
The information gathered by satellite cameras is used to understand and predict weather patterns. Satellite imaging is largely to thank for accurate weather prediction tools and can be used to predict natural disasters. This type of satellite weather camera is becoming increasingly important as the world learns to deal with the effects of climate change.
Climate change makes natural disasters more common and can cause disruption to normal weather cycles and seasonal patterns. Satellite camera technology can help communities to deal with this by predicting droughts, floods, and crop failures across continents. Having accurately gathered information about these changes from Earth observation projects can help us prepare for them.
Measuring biodiversity
Another ecological effect of climate change is the reduction in biodiversity in various ecosystems, such as in forests, jungles, or the ocean bed. Satellite cameras can help researchers to track biodiversity and witness the effects of climate shifts. This can help us uncover problem areas, predict problems before they occur, and come up with solutions on how to restore depleted areas.
Archaeological research
As well as monitoring ecological shifts, satellite imaging from space can help with other types of research. One common use for satellite cameras is to help locate archaeological dig sites and discover ancient ruins. Satellites can take pictures from great heights, allowing researchers to see a comprehensive scan of vast land areas. This then allows researchers and archaeologists to spot unusual formations on the landscape that might indicate an undiscovered site.
Improving shipping routes
Satellite images can also help lower carbon emissions by making supply chains more efficient. Photos from space can help shipping companies chart the fastest routes for delivering goods globally. This can help reduce fuel use and limit the damage caused to fragile ocean ecosystems by noise from shipping vessels.
Satellite cameras are vital for science
The use of satellite camera imaging is vital to many aspects of global research. From monitoring weather patterns to tracking species development, it is likely that society will rely on this technology even more in the future. Satellite cameras are also getting more varied in size, leading to greater opportunities for research.