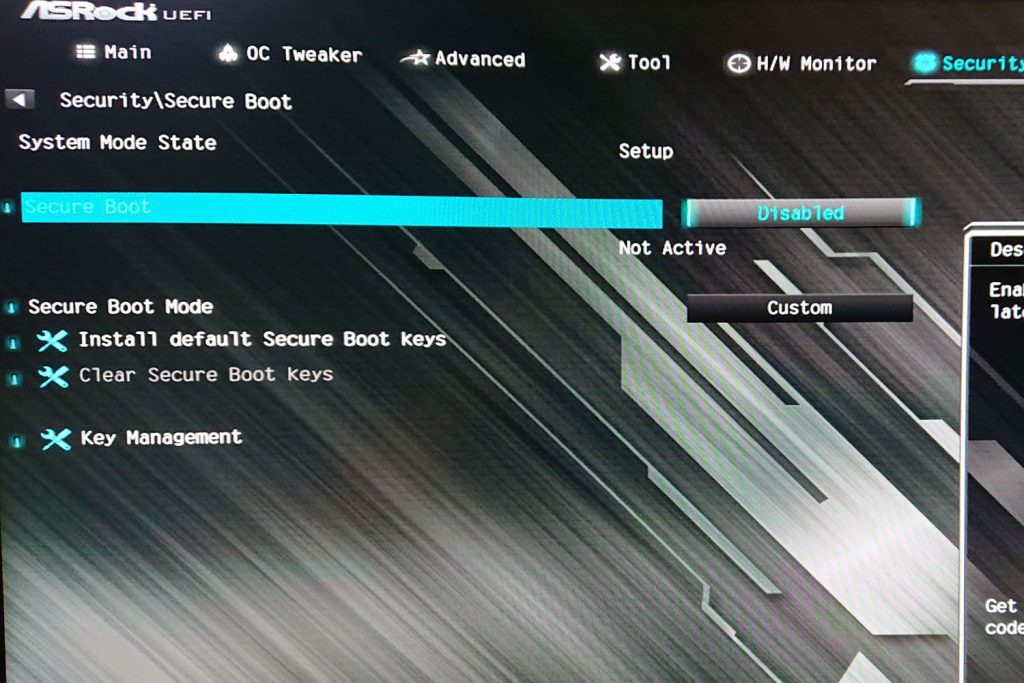
Microsoft’s Windows 10 and 8 operating systems, as well as a few Linux variants, all offer the Secure Boot safety mechanism. It is supposed to safeguard your system from bugs by confirming that a trustworthy source has authorized the application you are using. Let’s take a closer look at Secure Boot and know what it is and why we need it.
What Is Secure Boot?
Machines with Secure Boot are designed to guarantee that only trustworthy applications may be run on them. Any .exe applications would be verified for authenticity before being allowed to execute on the machine with Secure Boot activated. As a result, it is much more challenging for hackers to get possession of the computer via this validation procedure. With additional safety capabilities, including encrypting files and intrusion detection, Secure Boot may give a multi-layered strategy for protection.
This feature verifies the legitimacy of a desktop’s program, especially the os contents, utilizing a digital certificate. The digital certificate serves as a guarantee that the system software is authentic and has not been interfered with. Prior to signing, a certification issuer checks out the source code. Finally, the operating system is authenticated by a certified agency to ensure it has not been corrupted.
A digital signature would be issued by the certification body after the program has been authenticated. Secure Boot compatible systems may then launch the certified application. The digital certificate would be verified for authenticity before the program may be executed by the computer. If the system finds the aforementioned signature invalid, the computer would not permit the program to operate.
Why You Should Use It?
To safeguard your computer from viruses, you should enable Secure Boot. It is possible to protect the integrity of the applications you employ by simply permitting verified versions to execute. Although Safe Boot is not a comprehensive cybersecurity measure, it may assist to render your computer more secure by rendering it increasingly challenging for hackers to launch harmful programs on your computer.
This feature has the apparent drawback of making it more challenging to launch unregistered applications. It must be disabled if you want to execute unsigned applications on your computer. Secure Boot may also render it more challenging to run two operating systems at the same time. If you want to use an alternative bootloader and deactivate Secure Boot, you’ll require to do so. For most consumers, the advantages of Secure Boot far exceed the shortcomings of the technology.
You may use this feature to guarantee that only trustworthy applications are allowed to run on your computer. This feature may assist in avoid malware and other dangerous code from launching on your computer by checking the digital certificate of any application programs. It does have certain obvious risks, but the safety gains far exceed them for most consumers. Nevertheless, you may deactivate the option in BIOS options if you ever have to install unlicensed applications or dual-boot your laptop.