The RIKEN Guardian Robot Project in Japan has developed an android kid called Nikola that is capable of expressing all six of life’s fundamental feelings in a natural way. To see how effectively individuals could distinguish between six different emotions elicited by Nikola’s visage as he moved, the researchers published their findings in the journal Frontiers in Psychology.
These six emotions are the first to be examined and validated for the accuracy of android-expressed empathy.

Pneumatic Actuators Governs The Facial Expressions
For nearly half a century, Rosie has been deemed just speculative fiction when she appeared on Jetson’s television show. There are still numerous difficulties to overcome before the friendly robot becomes a real thing, along with the ability to sense and communicate feelings.
The RIKEN Guardian Robot Project’s Wataru Sato recently conducted research to develop an android, and humanoid robot that can portray a wide range of emotions via its face. Thus, Nikola was created looking like an artificial head resembling that of a little kid.
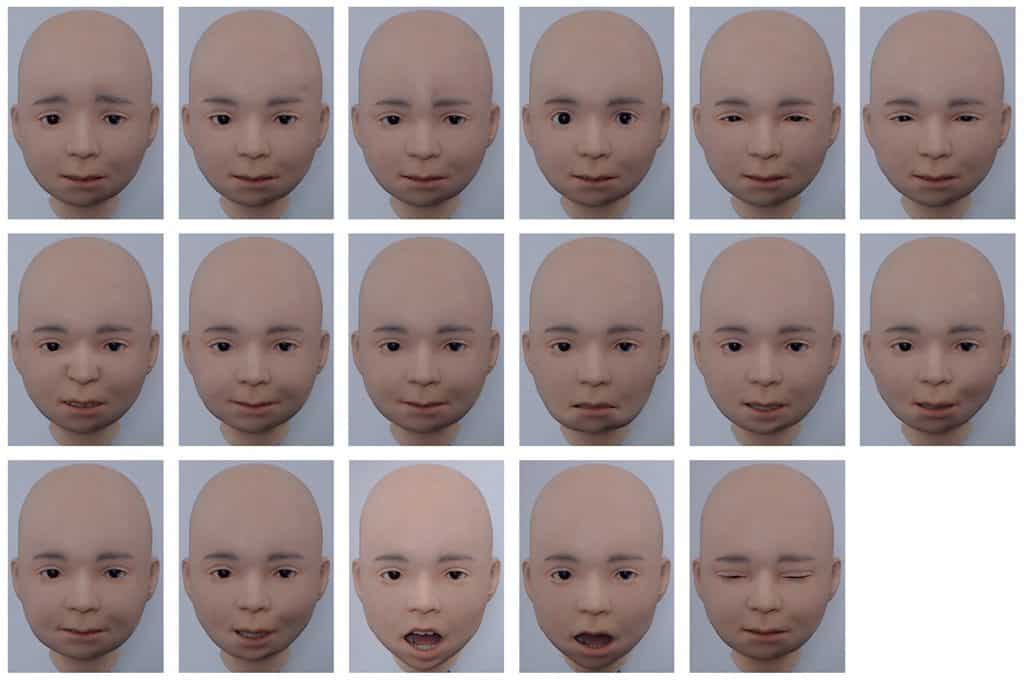
The researchers utilized the (FACS) alias Facial Action Coding System to determine where the actuators should be put. Various facial expression units, like the “cheek lifter” as well as the “lip pout,” have been found in previous studies and included in Nikola’s design to represent common emotions like pleasure or distaste.
Have You Read: Zuckerberg Says Meta Employees Will Now Be Called “Metamates”
There are a total of 29 pneumatic actuators fitted within Nikola’s visage that govern the mobility of synthetic face muscles. A further set of six actuators controls the motions of the eyes and the head. The smoothness and quietness of mobility are attributes of pneumatic actuators, which are powered by air pressure.
Nikola’s Emotions Resembles That of a Human Face
Nikola’s face motions mirror that of an actual human being, according to a professional trained in FACS grading. People were able to identify all six of Nikola’s basic emotions, although with varying degrees of success in a second test conducted by the researchers.
Due to the fact that Nikola’s silicone flesh is comparatively less stretchy than human tissue, it is unable to produce wrinkles. Since there was no reaction to nose creasing, feelings like contempt were difficult to discern.
“In the short term, androids like Nikola can be important research tools for social psychology or even social neuroscience.” “Compared with human confederates, androids are good at controlling behaviors and can facilitate rigorous empirical investigation of human social interactions.”
“Androids that can emotionally communicate with us will be useful in a wide range of real-life situations, such as caring for older people, and can promote human wellbeing,” says Sato.
For all intents and purposes, the prime objective of the Guardian Robot Study is to construct an artificial robot that can aid humans, especially those with physical requirements and who are living alone.


