In today’s data-driven world, organizations face the immense challenge of managing and protecting vast amounts of data. With data playing a critical role in decision-making, compliance, and innovation, organizations must establish robust practices to ensure data is effectively governed. In this article, we explore the concept of data governance, discussing its policies, processes, and frameworks that enable organizations to manage and protect data efficiently. So, let’s dive into the world of data governance and its significance in modern organizations.
Contents
Defining Data Governance
Data governance encompasses the strategies, policies, and processes that organizations implement to ensure the availability, integrity, security, and usability of their data assets. It provides a framework for defining who within the organization is responsible for data, how data should be managed, and what procedures should be followed to maintain data quality and compliance. Effective data governance ensures that data is treated as a valuable asset, allowing organizations to derive insights, make informed decisions, and maintain trust with stakeholders.
Data governance is essential for several reasons:
- Data Quality and Consistency: Data governance establishes standards and processes to ensure data accuracy, consistency, and reliability. By maintaining high-quality data, organizations can rely on accurate insights for decision-making, reducing errors and improving overall operational efficiency.
- Compliance and Risk Management: With the increasing regulatory landscape, organizations must adhere to data protection and privacy laws. Data governance frameworks help organizations define and enforce policies and procedures to ensure compliance, mitigating legal and reputational risks.
- Data Security and Privacy: Data governance ensures the implementation of appropriate security measures to protect sensitive and confidential data. By establishing access controls, encryption mechanisms, and data classification frameworks, organizations can safeguard data from unauthorized access, breaches, and potential data privacy violations.
- Data Integration and Interoperability: Organizations often deal with diverse data sources and systems. Data governance provides guidelines and standards for data integration, ensuring compatibility and consistency across different platforms. This enables seamless data sharing and collaboration within and outside the organization.
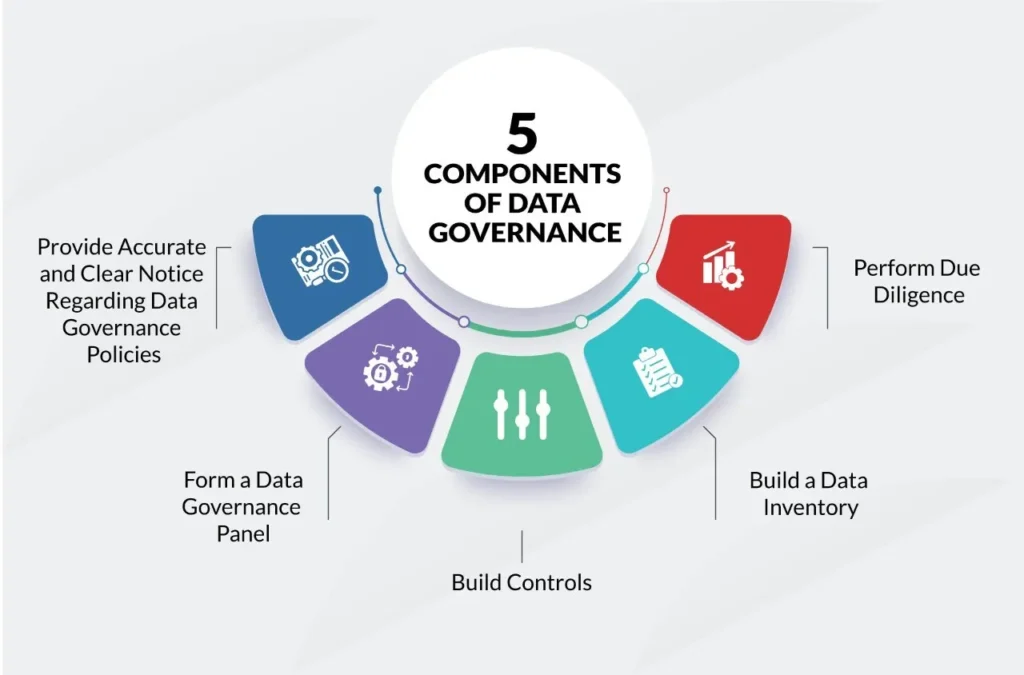
Components of Data Governance
To establish effective data governance, organizations must consider several key components:
- Data Governance Framework: A data governance framework outlines the structure, roles, and responsibilities within the organization for managing data. It defines decision-making processes, establishes data stewardship roles, and ensures alignment with organizational objectives.
- Data Policies and Standards: Data governance involves defining policies and standards for data management. These policies cover aspects such as data quality, data classification, data retention, data access, and data privacy. Standards provide guidelines for data naming conventions, data formats, and data documentation, ensuring consistency and understanding across the organization.
- Data Stewardship: Data stewardship involves assigning individuals or teams the responsibility for managing and maintaining data assets. Data stewards play a crucial role in enforcing data policies, resolving data-related issues, and ensuring data integrity throughout its lifecycle.
- Data Lifecycle Management: Data governance encompasses the management of data throughout its lifecycle, from creation to archival or disposal. This includes processes for data capture, storage, integration, transformation, and archival, with appropriate controls and documentation at each stage.
- Data Quality Management: Data governance includes processes for monitoring and improving data quality. This involves establishing data quality metrics, conducting data profiling, implementing data cleansing techniques, and continuously monitoring data to identify and rectify any quality issues.
- Data Security and Privacy: Data governance incorporates measures to protect data from unauthorized access, breaches, and misuse. This includes defining access controls, implementing encryption, conducting regular security audits, and ensuring compliance with data privacy regulations.
Implementing Data Governance
Implementing data governance requires a strategic and systematic approach:
- Define Objectives: Identify the objectives and outcomes you want to achieve through data governance. This could include improving data quality, enhancing compliance, or optimizing data management processes.
- Establish Governance Structure: Define the governance structure and assign roles and responsibilities to individuals or teams responsible for data governance. This includes data stewards, data owners, and executive sponsors.
- Develop Policies and Standards: Create data policies and standards that align with industry best practices, regulatory requirements, and organizational needs. Ensure these policies are communicated, understood, and enforced throughout the organization.
- Implement Processes and Procedures: Develop processes and procedures for data management, data quality management, data security, and privacy. Document these processes and ensure they are followed consistently.
- Monitor and Evaluate: Continuously monitor the effectiveness of data governance practices. Establish metrics to measure the success of data governance initiatives and make adjustments as needed.
Conclusion
Data governance is a critical aspect of modern organizations’ data management strategies. By implementing robust policies, processes, and frameworks, organizations can effectively manage and protect their data assets. Data governance ensures data quality, compliance with regulations, security, and privacy, enabling organizations to make informed decisions, drive innovation, and maintain stakeholder trust. Embracing data governance as a core organizational practice is essential for harnessing the true potential of data and thriving in today’s data-driven landscape.